Introduction
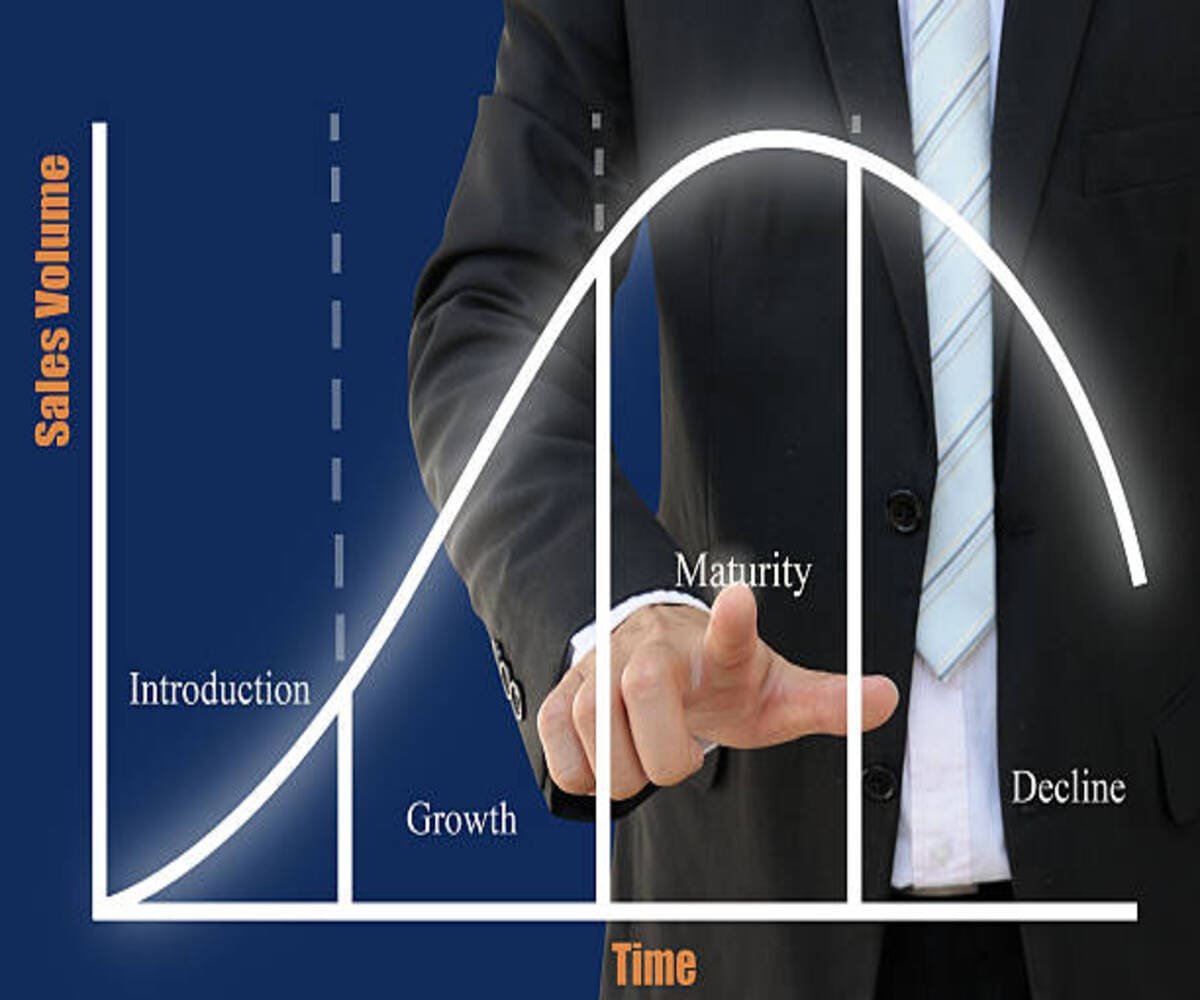
The Product Life Cycle (PLC) is a fundamental concept in marketing management that describes the various stages a product goes through from its introduction to its eventual decline. Understanding these stages helps businesses make informed decisions about marketing strategies, pricing, distribution, and product innovation.
This guide provides an in-depth explanation of the five stages of the product life cycle, their characteristics, and the best marketing strategies for each stage.
1. Introduction Stage
Definition:
The Introduction Stage is when a product is first launched into the market. Awareness is low, and businesses invest heavily in promotions to attract early adopters.
Key Characteristics:
✔ High marketing and promotional costs. ✔ Low or negative profitability due to initial expenses. ✔ Limited product availability and distribution. ✔ Customer awareness is still developing. ✔ Sales grow slowly as consumers become aware of the product.
Marketing Strategies:
✔ Market Penetration Pricing – Set a low price to gain market share quickly. ✔ Skimming Pricing – Set a high price initially to recover costs and attract early adopters. ✔ Intensive Advertising – Focus on digital marketing, social media, and influencer partnerships. ✔ Selective Distribution – Target niche markets and build brand credibility. ✔ Customer Education – Use content marketing, tutorials, and product demonstrations.
2. Growth Stage
Definition:
The Growth Stage is characterized by increasing demand, expanding market reach, and rising profits. Competitors may enter the market as the product gains popularity.
Key Characteristics:
✔ Sales volume increases rapidly. ✔ More competitors enter the market. ✔ Brand recognition improves. ✔ Production costs decrease due to economies of scale. ✔ Customer loyalty begins to develop.
Marketing Strategies:
✔ Expand Distribution Channels – Make the product widely available through online and offline stores. ✔ Competitive Pricing – Offer value-based pricing to maintain market share. ✔ Brand Differentiation – Highlight unique selling propositions (USPs) through targeted campaigns. ✔ Influencer & Referral Marketing – Leverage word-of-mouth and customer testimonials. ✔ Loyalty Programs & Discounts – Encourage repeat purchases and customer retention.
3. Maturity Stage
Definition:
The Maturity Stage is when a product reaches peak market penetration. Growth slows, but sales remain steady as the product has established a loyal customer base.
Key Characteristics:
✔ Market saturation occurs as most potential customers have purchased the product. ✔ Intense competition leads to price reductions. ✔ Profit margins may shrink due to competitive pricing. ✔ Companies focus on maintaining brand loyalty. ✔ Product innovation and differentiation become essential.
Marketing Strategies:
✔ Product Improvements & Variations – Introduce new features, packaging, or extensions. ✔ Rebranding & Market Expansion – Target new demographics or geographic regions. ✔ Strategic Partnerships – Collaborate with other brands for cross-promotions. ✔ Customer Engagement & Retention – Utilize personalized offers, email marketing, and loyalty programs. ✔ Cost Leadership Strategy – Optimize production to reduce costs and sustain profitability.
4. Decline Stage
Definition:
The Decline Stage occurs when market demand decreases, either due to changing consumer preferences, technological advancements, or the emergence of better alternatives.
Key Characteristics:
✔ Sales decline steadily. ✔ Companies cut down on marketing expenses. ✔ Product relevance decreases. ✔ Competitors may withdraw from the market. ✔ Profitability declines unless cost-cutting measures are taken.
Marketing Strategies:
✔ Product Diversification – Introduce improved versions or explore new market segments. ✔ Harvesting Strategy – Reduce investment while maintaining profitability for as long as possible. ✔ Discontinue or Pivot – Phase out the product and shift focus to newer offerings. ✔ Niche Marketing – Target a specific customer segment still interested in the product. ✔ Bundle Offers & Clearance Sales – Sell remaining inventory with promotional pricing.
5. Revival (Optional Stage)
Definition:
In some cases, a product can re-enter the market with modifications, repositioning, or a new marketing approach. This is common for brands that reintroduce classic products or adapt to new trends.
Marketing Strategies:
✔ Repackaging & Rebranding – Refresh the product’s look and messaging. ✔ New Target Audience – Appeal to a different demographic or generation. ✔ Technological Enhancements – Upgrade product features to meet modern demands. ✔ Limited Edition or Seasonal Releases – Create exclusivity to boost demand. ✔ Influencer & Celebrity Endorsements – Renew interest through brand ambassadors.
Conclusion
Understanding the Product Life Cycle enables businesses to adapt their marketing strategies for each stage, ensuring sustained growth and profitability. By leveraging data-driven insights, companies can optimize product offerings, engage with customers effectively, and stay ahead of the competition.
Enhance Your Marketing Strategy with SignifyHR
At SignifyHR, we help businesses navigate product life cycle stages with data-driven marketing strategies. Contact us today to maximize your product’s success and longevity!